EXTERNAL COUNTER PULSATION
External Counterpulsation (ECP- External Counterpulsation) is an FDA-cleared, non-invasive, non-surgical and outpatient medical therapy for the treatment of angina, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and cardiogenic shock.
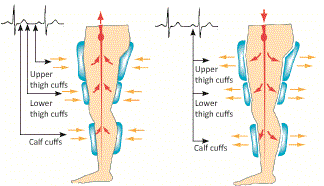
How is EECP/ECP therapy delivered?
The EECP/ECP systems consist of three sets of inflatable pressure cuffs wrapped around the calves and the lower and upper thighs, including the buttocks, as the patient lies down. In synchronization with each cardiac cycle, obtained with an integrated 3 electrode single channel ECG, the cuffs are sequentially inflated from the calves to the buttocks during diastole to produce an arterial retrograde flow towards the aortic root to increase coronary blood flow. EEC/ECP simultaneously increases venous return to raise cardiac output. The cuffs are deflated simultaneously before the onset of systole to provide an empty vascular space reducing systemic vascular resistance in the lower extremities to receive blood ejecting from the heart, significantly reducing the workload and oxygen demand of the heart.
In the process, ECP develops new pathways around blocked arteries in the heart by expanding networks of tiny blood vessels ("collaterals") that help increase and normalize blood flow to the heart muscle. For this reason, it is often called the NATURAL BYPASS.
What can ECP therapy do for you?
Angina
Angioplasty (PTCA) or Bypass surgery (CABG).
CAD – Coronary Artery Disease
CHD – Coronary Heart Disease
PVD – Peripheral Vascular Disease
ED – Erectile Dysfunction
Cardiac chest pain
Congestive heart failure
High blood pressure
Cardiomyopathy
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral vascular disease
Edema, or venous insufficiency
Chronic fatigue
Intestinal vascular insufficiency
Other benefits of ECP therapy includes:
Stroke
Parkinson's disease
kidney disease
Memory disorders
Diabetes and Diabetic Neuropathy
Cerebral palsy
Peripheral vascular disease
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Macular degeneration
Other circulatory diseases
hearing loss and tinnitus
vision impairment
autoimmune diseases (including Raynaud's phenomenon)
rheumatic disease
restless leg syndrome.
Sports Enhancement
Lymphatic System